주제 2 NIHSS 점수 예측

Scientific overview (연구 배경 및 중요성)
In determining the indications for revascularization during the acute treatment of stroke patients,
the clinical-diffusion mismatch is an important criterion for patients whose symptom onset
has passed 6 to 24 hours. The criterion for clinical-diffusion mismatch has been crudely
evaluated by considering an image-based criterion (i.e., lesion size according to age) and
a clinical-based criterion (i.e., National Institute of Health Stroke Scale; NIHSS score).
However, since the patient's symptoms and NIHSS score vary depending on the location of
the lesion, it is difficult to judge the indications for revascularization based on the
criterion (i.e., use of lesion size and NIHSS).
Recently, advanced interpretation techniques for clinical symptom using the clinical
images are proposed (e.g., radiomics and CNN). The MRI and machine learning techniques
may be feasible option for more accurate prediction of clinical symptom. Developed predictive
method for clinical symptom using the MRI from the challenge will be helpful in determining
the indications for revascularization of stroke patients from 6 to 24 hours after stroke or later.
Challenge questions (문제 정의)
Develop a predictive method to accurately interpret the National Institute of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score using the MRI scans (i.e., DWI)
Data description (데이터 설명 – 데이터 셋 구성, 형식, 특징)
Data collection from multi-center (4 institutes in South Korea) will be provided as the training and validation data for this year’s HeLP challenge - Stroke NIHSS Prediction.
- (1) Data Set : 339 of acute stroke patients (237 and 102 for Training and Validation, respectively)
- (2) Clinical Data and Label : NIHSS score (training data only)
- (3) Image Data : Diffusion-weighted MRI (DWI)
MRI scans were performed using 3 types of 1.5-T clinical whole body scanners from different vendors (Avanto, Siemens; Signa, GE Medical Systems; Achieva, Philips Medical Systems) with a standard head coil. For each patient, an acute stroke MRI protocol including DWI and FLAIR sequences was used in each center. ADC maps were automatically created from DWI scans using the built-in software. Therefore, the imaging parameters are different depending on institutes and vendors. Representative imaging parameters for each type of scanner are summarized in the Table below.
| GE Medical System | Philips Medical System | Siemens | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DWI | b-value (s/mm2) | 0 and 1,000 | ||
| TR (ms) / TE (ms) | 7,000 / 86 | 3,000 / 56 | 3,000 / 86 | |
| FOV (mm x mm) | 250 x 250 | |||
| Matrix size | 256 x 256 | 256 x 256 | 384 x 384 | |
| Number of slices | 20 | |||
| Slice thickness (mm) / gap (mm) | 5.0 / 2.0 | |||
Not provided.
The brain MRI images (i.e., DWI) are provided in compressed NifTi format (.nii.gz). Registration was applied using ANTs Toolbox: from its native space to Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) space with a resolution of 2 mm × 2 mm × 2 mm (91 x 109 x 91 voxel in x-, y-, and z-axis).
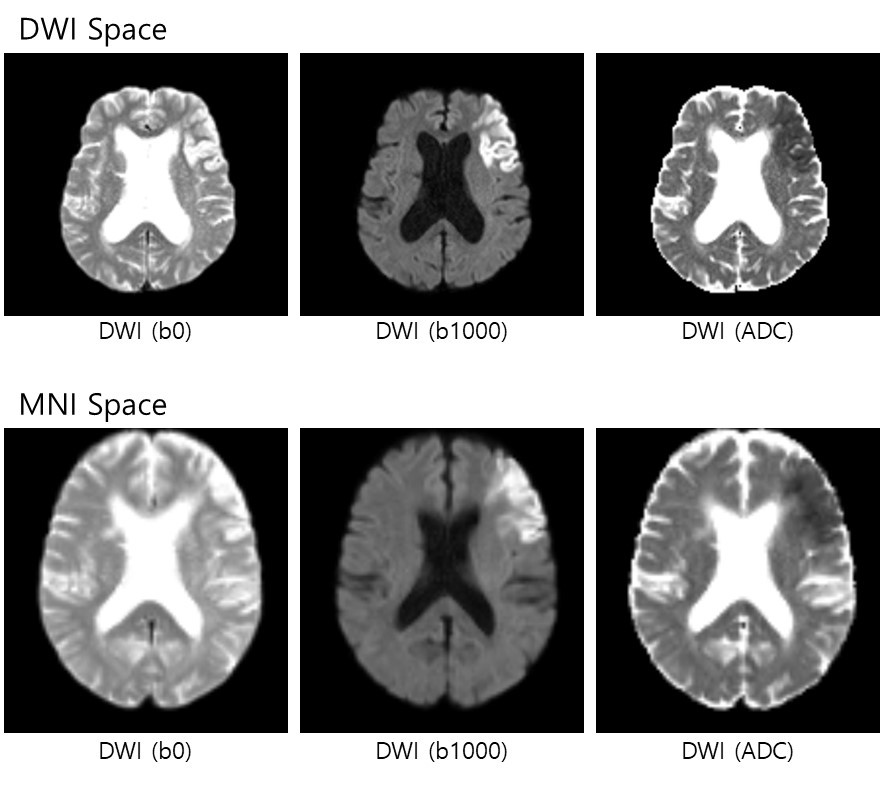
Each patient have two folders based on preprocessing (i.e., DWI space or MNI space). Each folder contains 3 files of images as followed:
[DWI_Space] Folder (3 files): Brain Extraction was applied.- (1) b0_brain.nii.gz
- (2) b1000_brain.nii.gz
- (3) adc_brain.nii.gz
- (1) b0_brain_MNI_iso2mm.nii.gz
- (2) b1000_brain_MNI_iso2mm.nii.gz
- (3) adc_brain_MNI_iso2mm.nii.gz
Evaluation matrix (정량적 평가 방법)
(1) Requirements for participants in submission (excel)
- Submit the predicted NIHSS score using own method (integer)
(2) Evaluation
- Root-mean-squared-error between submitted and labeled scores in validation data




